India is one of the South Asian countries with the second largest population globally. Geographically, it is the seventh-largest country. It is the largest democracy in the world. Several countries and the Himalayan range of mountains act as barriers to these countries border it. Militarily, it has often faced problems from these neighbours and tries its best to maintain cordial relations with them. Which are the countries that border India?
Countries that Border India
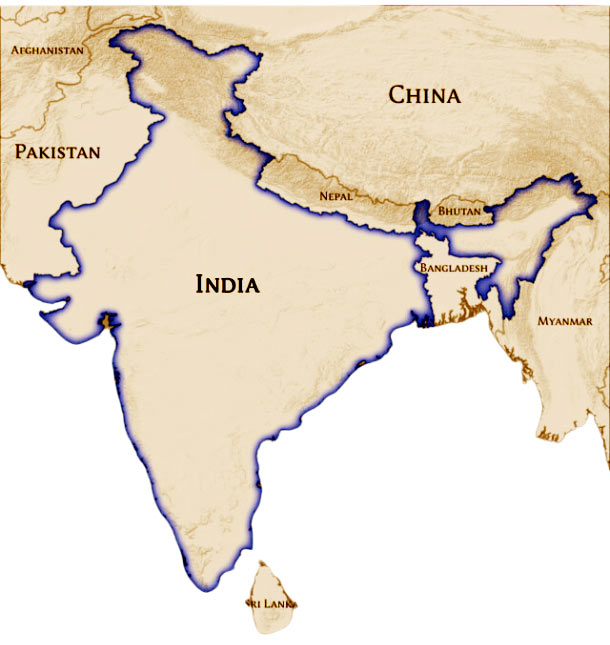
China
This is a powerful nation and is led by a communist regime. It is situated in the Northern part of the Himalayas and has the largest population in the world. The political philosophy adhered to by the Chinese is much different from that of India, which is a democracy. India has been at war with China and has border disputes. Diplomatic ties between China and India are often strained for geopolitical reasons. China is a threat to the peace prevailing in India. The trade and economic interactions between the two countries are complex and significant.
Pakistan
This is in the northern-western region of the Himalayas and has always been at loggerheads with India over border disputes. It has been mostly led by a military dictatorship, which does not gel with the liberal democratic philosophy of the Indian Government. Earlier, Pakistan was part of India, but after the independence of India, Pakistan was formed as a separate Muslim nation. Pakistan has also been at war with India. The relationship between India and Pakistan has significant regional security and stability implications.
Bangladesh
This is in the eastern region of India and was part of Bengal. It consists mostly of the Muslim population. People speak Bengali, and culturally, they are closer to West Bengal in India. It became a separate state after a prolonged war. The bilateral relationship between India and Bangladesh has evolved into a significant partnership, particularly in trade and connectivity.
Tibet
This is an autonomous region in China. The Chinese government is accused of persecuting the local people. Tibet is in much political controversy. Many Tibetans have settled in India as refugees. The Tibetan government in exile is being led by Dalai Lama, who considers Tibet to be a sovereign country occupied by the Chinese military. Dalai Lama wants Tibet to be an autonomous region. He needs to seek full independence for it. India’s support for the Tibetan community and the Dalai Lama remains a sensitive issue in Sino-Indian relations.
Nepal
It is north of the Himalayan range. It has been a monarchy throughout history, although now the Maoists have been asserting. A civil war between the monarchist forces and the communists led to the abdication of the then ruling King, Gyanendra. It is now a federal democratic republic since 2008. India maintains cordial relations with it. The Indo-Nepal relationship is marked by cultural and historical ties that influence political and economic interactions.
Burma
The region is also known as the Myanmar region, as a military-led government runs it. Historically, it has been at the forefront of the political arena. India and Burma share a long land border and a range of bilateral relations, including economic, cultural, and strategic aspects.
Bhutan
It is bordered East and West by India. It is separated from Nepal by the Indian state of Sikkim. It was one of the most isolated nations in the world, but now much development is taking place. It is known for its landscape. Buddhism is the predominant religion, although Hinduism is the second-largest religion. Its first democratic elections were held in 2008. Bhutan’s unique approach to development, emphasizing Gross National Happiness, has garnered international interest.
Sri Lanka
This is located south of India. Historically, Sri Lanka and India had many dealings with each other. It is the centre of the Buddhist religion. It strategically links Southeast Asia with the West. It is a multi-religious and multi-ethnic country. The government is a mixture of parliamentary and presidential systems. The relationship between India and Sri Lanka is characterized by shared religious and cultural heritage and geopolitical interests.
India tries to maintain peace in the region by preserving friendship with its neighbours. Of course, disputes sometimes arise, making it difficult to settle the issue through diplomatic ties. The peace within the country is often threatened by its neighbours.